|
PartitionMagic v. 3.03 (3/3/1997, PowerQuest Corporation) |
Readme/What's new |
PartitionMagic by PowerQuest
Version 3.03
Copyright (c) 1994-1997, PowerQuest Corporation
All Rights Reserved. Patents Pending.
This file explains changes made since the printing of the manual.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
-----------------
1. License Types
2. Updates
3. Technical Support Issues
4. General Usage Notes
5. FAT32 Usage Notes
6. Boot Manager vs. PQ Boot
7. Windows NT and the Partition Copy function
8. UnInstaller Mover by MicroHelp
9. Partition Magician Newsletter
1. License Types
----------------
The Personal License Version is a machine-specific license that allows
modifications on one specific computer. See the *User Guide* for the license
agreement.
The Pack License Version is available for use on a specific number of
computers; refer to the specific license for the number of active users
allowed.
The Professional License Version is available for modifying an unlimited
number of computers, one computer at a time.
The Enterprise Version is available for organizations requiring remote or
unattended configuration capabilities at multiple sites.
For information on the Pack, Professional or Enterprise Versions of
PartitionMagic, contact PowerQuest Corporate Sales at (801) 226-8977.
2. Updates
----------
To consistently give you the best available version of PartitionMagic, minor
updates are provided periodically. We recommend that you check regularly our
home page (www.powerquest.com), FTP site (ftp.powerquest.com), BBS
(801-226-5608) or CompuServe (OS2AVENDOR, Other Vendors section) for the
latest bug fixes and minor improvements.
3. Technical Support Issues
---------------------------
A. To run PartitionMagic 3.0 on a computer that has ONLY Windows NT do the
following:
-Boot the computer into Windows NT.
-Install PartitionMagic 3.0 to the hard drive.
-Create a bootable DOS floppy diskette.
-Copy PQMAGICT.EXE (PartitionMagic text mode version) to the bootable DOS
diskette.
-Exit Windows NT, reboot your computer using the DOS bootable diskette, type
A:\PQMAGICT and press Enter.
B. If you are unable to access your CD-ROM drive after partitioning your hard
drive see page 173 in the PartitionMagic 3.0 manual.
C. If PartitionMagic does not start properly or your computer locks up when
starting PartitionMagic see page 170 in the PartitionMagic manual for
information on freeing up conventional memory. If the steps listed on page
170 do not solve the problem, try running PartitionMagic with the /NSS switch
(PQMAGIC /NSS).
D. If you are receiving Error #110 and have an HP Pavilion, HP Vectra or
Digital Computer, please run PARTINFO according to the instructions on page
197 in the PartitionMagic 3.0 manual and contact PowerQuest Technical
Support (801-226-6834) for instructions on how to solve the problem.
4. General Usage Notes
----------------------
- Don't forget to backup your hard drive before using PartitionMagic. While
PartitionMagic has been thoroughly tested and is quite safe, power failure,
operating system bugs, and hardware design bugs can put your data at risk. No
software program, including PartitionMagic, is perfect. Before using any
utility that makes such extensive changes to your hard drive, you should
backup your data.
- If you use Windows 3.1 and find that your mouse does not work in
PartitionMagic, a Microsoft compatible mouse driver is supplied with
PartitionMagic. To access the mouse driver exit to DOS and type
"C:\PQMAGIC\MOUSE" or insert this line in your AUTOEXEC.BAT file.
- If you run PartitionMagic from DOS: Turn off 3rd party disk caches.
Deactivate or unload any TSR programs that access or modify the partitions
being changed. Do not run PartitionMagic from a compressed drive.
- After using PartitionMagic, it is normal to get an error message when
starting Windows 3.1 stating that the swap file is corrupt. Windows 3.1 is
designed knowing that disk utilities may move the clusters of the swap file.
When a move is detected, the error message is given. To fix the swap file,
click on the 386 Enhanced icon in Control Panel, then on the Virtual Memory
button then delete the swap file and create it again.
- This release of PartitionMagic handles ASCII filenames. PartitionMagic
does not yet handle double byte character sets such as Japanese, resulting in
two known limitations: (1) Converting a partition from FAT to HPFS can
produce incorrectly translated filenames. (2) An attempt to specify or set
the Volume label may fail.
- Sometimes changes made by PartitionMagic confuse Windows NT 3.5x, which
then assigns drive letters incorrectly. This bug is fixed in Windows NT 4.0.
NT 3.5x users should use Disk Administrator to assign the drive letters back
to the values you prefer.
- Progress bars are an estimation only and can pause for several minutes,
even though PartitionMagic is still working correctly. If you think your
computer has locked up, please be patient and PartitionMagic will finish the
operation.
5. FAT32 Usage Notes
--------------------
- The following operating systems support FAT32:
Windows 95B - OSR2
Windows 97
- If you are using an Operating System that supports FAT32 together with an
operating system that doesn't support FAT32 (i.e. Windows 3.11, Windows 95,
Windows NT) you may wish to disable FAT32 support. Operating systems that
don't support FAT32 will be unable to see FAT32 partitions. FAT32 support
can be set in the preferences.
- OS/2 does not support FAT32 partitions. Also, if you convert a partition
to FAT32 and convert it back to FAT16, all OS/2 extended attributes (EAs)
will be lost.
- The minimum size for a FAT32 partition is about 260 MB.
- Please note that the memory requirement (16 MB) for modifying FAT32
partitions is true in most circumstances. However, in some extraordinary
circumstances more memory may be required.
6. Boot Manager vs. PQ Boot
---------------------------
PartitionMagic 3.03 ships with both Boot Manager by IBM and PQ Boot by
PowerQuest.
When you install Boot Manager, PartitionMagic will create a separate primary
partition and mark it active. When the computer starts, Boot Manager
displays a startup menu that allows you to choose the partition to boot.
PQ Boot is a command line utility to switch between bootable primary
partitions. When a primary partition is selected using PQ Boot, it is set
active and PQ Boot reboots the computer.
Both boot utilities are useful for different situations. For example, Boot
Manager requires an additional primary partition while PQ Boot does not. Boot
Manager allows you to choose which operating system to boot each time you
start your computer. PQ Boot, on the other hand, is ideal for users who will
only occasionally change the active partition. Boot Manager allows OS/2
installation to a logical partition and can boot OS/2 and a few other
operating systems from a logical partition. PQ Boot will only boot primary
partitions.
If both are used together, using PQ Boot to boot a partition other than Boot
Manager will deactivate Boot Manager. To reactivate it, use PQ Boot,
PartitionMagic or some other method to set Boot Manager as the active
partition.
Boot Manager will not correctly boot from a FAT32 partition if other primary
FAT/FAT32 partitions are present. To boot a FAT32 partition, set it active
with PartitionMagic or with PQ Boot.
7. Windows NT and the PartitionCopy function
---------------------------------------------
PowerQuest's PartitionMagic does not update the Windows NT BOOT.INI file in
either the source or destination partition after a Copy operation. Therefore
Windows NT may NOT boot from the new copy. To make the partition bootable,
you must fix the BOOT.INI file to point to the new partition.
Also, a Copy Operation does not update drive letter references in the
destination partition Registry. You must fix some (not all) driver letter
references in the Registry. Fixing the drive letter references is
non-trivial and we do not recommend it.
8. UnInstaller Mover by MicroHelp
----------------------------------
For all UnInstaller Mover technical support questions, please contact
MicroHelp between the hours of 9 a.m. and 5 p.m., Eastern Standard Time at
(770) 591-6448 or send e-mail to tech@microhelp.com.
9. Partition Magician Newsletter
---------------------------------
PowerQuest has a monthly electronic newsletter that is dedicated to official
announcements regarding PartitionMagic. Signing up on the list will give you
all the information you need regarding product tips, bugs, and patches. Just
go to our home page (www.powerquest.com), enter your email address into the
space provided and hit the "Sign me up" button. You will be e-mailed a
response verifying your subscription. |
|
PartitionMagic v. 1.02 (17/4/1995, PowerQuest Corporation) |
Readme/What's new |
README.TXT for PartitionMagic
PartitionMagic by PowerQuest
Version 1.02 for OS/2
Copyright (c) 1994-1995, PowerQuest Corporation
All Rights Reserved. Patent Pending.
This file explains changes made since the printing of the manual.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
-----------------
I. Legal Notices
II. Changing Your Boot Partition
III. Boot Manager/FDISK Bugs
IV. OS/2 DMA Bug Can Destroy Data
V. Warnings
VI. Drives >1024 Cylinders
VII Text Mode PQMAGICT.EXE
VIII. Code Pages
IX. Error Messages
I. Legal Notices
----------------
The entire risk of the use or the result of the use of this software and
documentation remains with the user. No part of this document may be
reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
mechanical, for any purpose, except as expressed in the Software License
Agreement.
Copyright (c) 1994-1995, PowerQuest Corporation. All rights reserved. This
software and documentation are copyrighted. All other rights, including
ownership of the software, are reserved to PowerQuest Corporation. This
software is protected by one or more pending patents.
PartitionMagic, PowerQuest, the PowerQuest Mark, Partition Map, and Partition
List are trademarks of PowerQuest Corporation.
II. Changing Your Boot Partition
--------------------------------
If you want to modify your OS/2 boot partition, you must boot from an
alternate source. If you have multiple boot partitions, boot from a partition
other than the partition you want to modify. If your hard drive contains less
than 1024 cylinders, you can start and operate PartitionMagic from DOS. See
p. 19 in the *User Guide*. A step should be added between steps 1 and 2:
Change to the directory where PartitionMagic is installed, or change to a copy
of the 2nd installation diskette (the one containing PQMAGICD.EXE and
PQDPM.DAT).
You can also use PartitionMagic from OS/2 Maintenance Mode. See p. 19 in the
*User Guide*. When booting Warp, a change is made to step 3: press F3
instead of ESC to enter Maintenance Mode.
Also, see the material later in this file for information about drives
containing more than 1024 cylinders, and Text Mode (PQMAGICT.EXE).
III. Boot Manager/FDISK Bugs
----------------------------
Because of bugs and limitations in OS/2's Boot Manager, moving or resizing a
partition usually causes Boot Manager to malfunction. Boot Manager may delete
partitions from its menu, display partitions with the wrong drive letter, fail
to boot a bootable partition, fail to display a partition, or boot partly from
one partition and partly from another.
We have reported the problems to IBM and hope for their cooperation in finding
permanent solutions to these problems. In the mean time, the work-around is
simple. If you experience any of the above problems with Boot Manager:
1) Boot OS/2. If Boot Manager will not boot, you can boot from your
installation disks.
2) Run FDISK. FDISK does not suffer from the Boot Manager bugs and will
display all your partitions, with the correct drive letters.
3) For any partition that disappeared from the Boot Manager menu, select Add
to Boot Manager Menu. If that option is grayed out, first select Delete from
Boot Manager Menu. This works around Boot Manager's limitation: it can not
track moving partitions.
4) Otherwise, select Change Partition Name on any of the bootable
partitions. This works around Boot Managers bugs: Boot Manager sometimes
displays the wrong drive letter, fails to boot a bootable partition, fails to
display a partition, or boots partly from one partition and partly from
another.
5) Exit FDISK and save the changes.
There is another Boot Manager/FDISK bug that PartitionMagic detects and
handles automatically. Changing the Boot Manager label of a logical partition
using FDISK partially damages the partition tables. The damaged portions are
non-critical for DOS and OS/2. PartitionMagic used to give error 108,
"Partition doesn't end at end of cylinder" when detecting the damaged tables.
Then PartitionMagic would refuse to run. PartitionMagic now diagnoses the
damage and extracts the proper information from other sources in the partition
tables. If PartitionMagic makes any changes to the logical drive associated
with the damaged partition table, PartitionMagic will write a repaired table
to the disk.
Another FDISK bug that PartitionMagic detects is more serious. If free space
exists within the extended partition (typically as a result of using DOS's
FDISK), OS/2's FDISK will allow creation of a primary that overlaps the
extended partition. Subsequently using DOS's FDISK allows creation of a
logical drive in the same space occupied by the overlapping primary.
PartitionMagic reports Error #113 when this situation is detected. Because of
the seriousness of this error, PartitionMagic will not allow any manipulation
of a physical drive containing this error. See Error #113, explained later in
this file. To avoid this OS/2 FDISK bug, never leave unused free space inside
the extended partition. PartitionMagic is particularly useful for resizing the
extended partition to avoid this problem.
IV. OS/2 DMA Bug Can Destroy Data
---------------------------------
We have found a bug in OS/2 that can cause corruption of your hard drive. We
have not determined whether the bug is an OS/2 software bug or a hardware
design bug that only affects OS/2. We have tested OS/2, DOS, Windows, Windows
95, and Windows NT; only OS/2 exhibits the bug. Whether software or hardware,
the effect on your data is the same: it gets destroyed!
During DMA transfers one data word is sometimes dropped, shifting all data by
two or four bytes. In an extreme case, if important file system or partition
data is lost, you can lose all data on the drive. This bug has nothing to do
with PartitionMagic. If you have the bug, your data is at risk whether you
use PartitionMagic or not. PLEASE DO NOT USE PARTITIONMAGIC IF YOU HAVE THIS
BUG!
The following procedure should diagnose if your machine has the bug. Type in
these two command files:
FILE1.CMD
---------
:START
COPY C:\OS2\DLL\TUTORMRI.DLL C:\DELETE.ME
COMP C:\OS2\DLL\TUTORMRI.DLL C:\DELETE.ME
GOTO START
FILE2.CMD
---------
:START
COPY C:\OS2\DLL\TUTORMRI.DLL A:\DELETE.ME
GOTO START
Run each command file in a different OS/2 command window. When FILE1.CMD asks
if you wish to compare more files, reply "N". If your machine has the DMA
problem, COMP will report comparison errors. If you do not have
C:\OS2\DLL\TUTORMRI.DLL, pick some other large file that will fit on a floppy.
One customer reported that this scenario did not show his problem, but copying
and comparing many small files did show his machine had a problem.
Dick Goran has graciously written a REXX program, TEST164.CMD, to do much the
same thing as the above command files. Our thanks to Dick. TEST164.CMD is
included with PartitionMagic.
We have found that on machines like the Gateway2000 P5-75 with AMIBIOS Version
1.00.10AX1T, a work-around is possible. In the BIOS setup, Advanced, Advanced
Chipset, PCI IDE Prefetch Buffers should be set to Disabled. We have seen the
bug on non-Gateway machines, PCI and VL bus machines, and non-AMI BIOS
machines. The machines have all had enhanced IDE controllers. As we learn
more about this bug, we will post messages in the CompuServe IBM OS/2 Users
Forum (OS2USER).
V. Warnings
-----------
- Don't forget to backup your hard drive before using PartitionMagic. While
PartitionMagic has been thoroughly tested and is quite safe, power failure,
operating system bugs, and hardware design bugs can put your data at risk. No
software program, including PartitionMagic, is perfect. Before using any
utility that makes such extensive changes to your hard drive, you should
backup your data.
- Don't powerdown or prematurely reboot when PartitionMagic is in the middle
of an operation.
- Do not use the DOS executable of PartitionMagic under Multitasking software
such as Windows or DesqView. It is best to turn off disk caching software when
using the DOS executable. When running PartitionMagic (DOS executable) under
Windows 95, please use MS-DOS Mode to prevent multitasking.
- It is normal to get an error starting Windows 3.1 stating the swap file is
corrupt. Windows 3.1 is designed knowing that disk utilities may move the
clusters of the swap file. When a move is detected, the error message is
given. To fix the swap file, delete the swap file and create it again. Click
on the 386 Enhanced icon in Control Panel, then on the Virtual Memory button.
- The PartitionMagic DOS executable (PQMAGICD.EXE) uses the same DOS extender
as DOOM. If DOOM will not run on your computer, chances are that PQMAGICD.EXE
will not run either.
VI. Drives >1024 Cylinders
--------------------------
If any partitions go past cylinder 1023, you will get error 109, "Partition
ends after end of disk" when running PartitionMagic from DOS or sometimes from
Maintenance Mode. If at all possible, use the Presentation Manager executable
(PQMAGIC.EXE) to modify the drive. Usually in OS/2 Maintenance Mode OS/2 can
access the entire drive. However, if the default driver set loaded for
maintenance mode does not include the drivers necessary for your drive, you
will not be able to access the entire drive until you modify the CONFIG.SYS
used to boot maintenance mode. Change the CONFIG.SYS used to start
Maintenance Mode to include the same hard disk drivers used by the full OS/2
boot.
VII. Text Mode PQMAGICT.EXE
---------------------------
When you run PartitionMagic in Maintenance Mode, depending on how you started
OS/2, you may get the error, "SYS1804: The system can not find the file
VIOCALLS." To solve this problem, copy VIOCALLS.DLL and PQMAGICT.EXE to a
scratch floppy. Then start PQMAGICT.EXE from the scratch floppy.
You should copy VIOCALLS.DLL from the disk or diskettes you used to boot OS/2.
It can be found in the following locations:
Boot Source VIOCALLS.DLL Location
---------------------- ---------------------
Installation Diskettes Install Disk 1
Utility Diskettes Utility Disk 2
Hard Disk \OS2\DLL
To access physical drives beyond the first four, use the Text Mode executable,
PQMAGICT.EXE.
VIII. Code Pages
----------------
This release of PartitionMagic handles 7-bit ASCII filenames. PartitionMagic
does not yet handle full 8-bit character sets such as Code Page 850 or double
byte character sets. Converting a partition can produce incorrectly translated
filenames.
IX. Error Messages
------------------
The following paragraphs explain the meaning of some of the error messages you
will encounter when using PartitionMagic. Some of these messages have been
added since the manual printing. Only the most common errors are explained
here.
Many errors can occur after selecting the Check option, or at the start of a
Move, Resize, or Convert operation before any changes are made to the
partition. If PartitionMagic detects a problem with a partition, it will
refuse to make any changes to it. Any changes made may decrease the amount of
data that can be recovered from the partition. This gives the maximum
protection to your data.
If an error is detected, exit PartitionMagic and run OS/2's CHKDSK (without
/F) on the same partition to further diagnose the problem. OS/2's CHKDSK
should be used instead of DOS's in order to detect problems in extended
attributes. If PartitionMagic's Check shows a problem and OS/2's CHKDSK does
not, either PartitionMagic has detected an error that OS/2 ignores, or
PartitionMagic has made a mistake. Either way, you should contact PowerQuest.
More likely, CHKDSK will detect the same problem that PartitionMagic did. If
you don't have a backup of your disk, now would be a good time to make
one. Then use CHKDSK /F on that partition to fix the problem. CHKDSK has many
bugs and can create more problems while solving others. After running CHKDSK
/F, try running CHKDSK (without /F) afterwards to make certain the partition
is fixed. CHKDSK should pass twice in a row before proceeding. Once CHKDSK is
satisfied that the partition is clean, use PartitionMagic's Check. If
PartitionMagic still shows a problem, CHKDSK /F may have introduced more
problems. At this point, you should re-format the drive and restore your files
from the backup.
PartitionMagic also performs a Check at the end of a Move, Resize, or Convert.
If the final Check fails, please report the problem to PowerQuest. In this
situation, data loss is not typical, but it is possible. Typically, the error
is a minor file system error easily corrected by CHKDSK /F. For more extensive
errors, you may need to restore from a backup.
Error Table
-----------
Error #3 - Not enough memory
The PartitionMagic box and manual explain the memory requirements of
PartitionMagic. Quitting other applications can sometimes free enough memory
for PartitionMagic to run.
Error #8 - Could not allocate/deallocate DOS real mode memory
PartitionMagic DOS executables use a DOS extender to make it possible for
PartitionMagic, which is a 32-bit application, to run from DOS. To read and
write the disk, PartitionMagic needs some memory in the first 1 MBytes of the
computers address space. If not enough memory is available, PartitionMagic can
not access the disk. Use the DOS MEM command to diagnose how much memory you
have available and what programs are using it. If you press F6 while booting
DOS, you will be asked whether to execute or not each CONFIG.SYS/AUTOEXEC.BAT
command. By skipping drivers or TSR programs that use memory, you can force
DOS to boot with more memory available.
Error #23 - Unsupported version of operating system
The PartitionMagic box and manual explain what version of the operating system
is required to run PartitionMagic. For most operating systems, the VER command
can be used in a command window to ask the operating system what version is
running.
Error #26 - xxxxx.DAT not found
The DOS executables require a data file containing the user interface objects
to be located in the same directory as the executable. PQMAGICD.EXE requires
PQDPM.DAT and PQMAGICW.EXE requires PQDWIN.DAT. Other executables require a
data file for the Help information. If you received this message when
pressing a Help button, the file PQHELP.DAT was not found.
Error #27 - Cannot lock drive
Under multitasking operating systems such as OS/2 and Windows 95,
PartitionMagic must lock a partition before it can safely make changes to it.
If PartitionMagic can not lock the drive, the drive has files that are being
held open by another process. Any programs currently running, including the
operating system, have open files. The boot partition typically has many open
files. Files listed in CONFIG.SYS (and sometimes AUTOEXEC.BAT) are often
open. The virtual memory swap file is open. See "Changing Your Boot
Partition," earlier in this file for information on how to run PartitionMagic
to avoid this error.
Error #34 - This Beta version is no longer safe to use
From time to time, PowerQuest releases beta versions of PartitionMagic. Beta
versions, by nature, are not as safe as the release versions. It is easy to
accidentally run a beta version when you think you are running a safe version.
To prevent accidental beta use, PowerQuest builds an expiration date into each
beta. After a reasonable test period, the beta will no longer function.
Error #36 - DPMI Server error
PartitionMagic DOS executables use a DOS extender to make it possible for
PartitionMagic, which is a 32-bit application, to run from DOS. This error
indicates that the DOS error has failed during a call from PartitionMagic
through the DOS extender to DOS (or the BIOS). DOS extenders often have
conflicts with extended memory users loaded in CONFIG.SYS or AUTOEXEC.BAT. If
you press F6 while booting DOS, you will be asked whether to execute or not
each CONFIG.SYS/AUTOEXEC.BAT command. By skipping all or most commands, you
can typically find a configuration that allows the DOS extender to run without
error.
Error #37 - File or app is open on partition
Under multitasking operating systems such as OS/2 and Windows 95,
PartitionMagic must lock a partition before it can safely make changes to it.
If PartitionMagic can not lock the drive, the drive has files that are being
held open by another process. Any programs currently running, including the
operating system, have open files. The boot partition typically has many open
files. Files listed in CONFIG.SYS (and sometimes AUTOEXEC.BAT) are often
open. The virtual memory swap file is open. See "Changing Your Boot
Partition," earlier in this file for information on how to run PartitionMagic
to avoid this error.
Error #38 - Program is running from that partition
You have selected an operation that changes the partition that PartitionMagic
resides on. Copy the PartitionMagic, along with any necessary .DAT files (see
Error #26), to a different partition (or a floppy disk). Then run from that
disk.
Error #40 - A hard disk is present but can't be accessed
Error #41 - Can not write, disk is write protected
Error #42 - Disk changed since last operation
Error #43 - Unknown unit
Error #44 - Drive not ready
Error #45 - CRC error in data
Error #46 - Seek error
Error #47 - Unknown media type
Error #48 - Sector not found
Error #49 - Write fault
Error #50 - Read fault
Error #51 - General hard disk failure
Error #52 - DMA error
Error #53 - Lock violation
Error #54 - Network device fault
Error #55 - Specified drive is busy
Error #56 - Unexpected internal error
These errors indicate that I/O with your disk was not possible. This usually
indicates hardware problems with the disk. Whenever possible, PartitionMagic
detects these errors before any changes have actually been made so that you
can backup your data before upgrading to a newer disk.
Error #100 - Partition table is bad
The hard drive partition table contains erroneous values. The partition
tables in the Master Boot Record (MBR) and Extended Partition Boot Records
(EPBR) can each contain one partition of type 5. If any single partition
table contains two 5 entries, this error occurs. Any changes PartitionMagic
makes may decrease the amount of data recoverable from the drive. Therefore,
PartitionMagic refuses to recognize any partitions on the drive. You may use
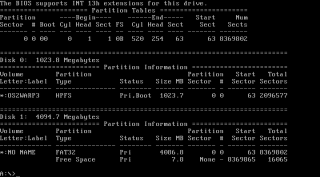
the PARTINFO utility program to print the contents of the partition tables.
Backup the offending partitions, delete and create them again, and then
restore the partition contents. This will create new, error-free
partition tables. You may need to use the FDISK from a fairly new
version of DOS. OS/2's FDISK will often see the same corruption that
PartitionMagic sees and silently refuse to make changes. Older versions of
DOS's FDISK may refuse to delete HPFS or hidden partitions.
Error #104 - No sectors in partition
It is not expected that any partition will contain zero sectors. Delete the
partition before using PartitionMagic.
Error #105 - Partition starts on wrong boundary
The hard drive partition table contains erroneous values. PartitionMagic
expects FAT, HPFS, and NTFS to begin and end on the boundaries used by FDISK.
If they do not, the disk may be partially corrupt and any changes
PartitionMagic makes may decrease the amount of data recoverable from the
drive. Therefore, PartitionMagic refuses to recognize any partitions on the
drive. You may use the PARTINFO utility program to print the contents of the
partition tables.
Backup the offending partitions, delete and create them again, and then
restore the partition contents. This will create new, error-free
partition tables. You may need to use the FDISK from a fairly new
version of DOS. OS/2's FDISK will often see the same corruption that
PartitionMagic sees and silently refuse to make changes. Older versions of
DOS's FDISK may refuse to delete HPFS or hidden partitions.
Error #106 - Partition doesn't start with sector one
See error #105.
Error #107 - Partition begins after end of disk
See error #109.
Error #108 - Partition doesn't end at end of cylinder
See error #105.
Error #109 - Partition ends after end of disk
Sometimes this error occurs when running one executable (such as PQMAGICD) but
does not occur when others (such as PQMAGIC or PQMAGICT). This is typically
the case for a drive using more than 1024 cylinders. Under DOS,
PartitionMagic is limited by the BIOS 1024 cylinder limit. If any partitions
extend past the limit, PartitionMagic can not safely operate on the drive. In
these instances, you must use the OS/2 executables (PQMAGIC or PQMAGICT) to
operate on the drive.
This error can also occur if a partition erroneously extends beyond the actual
end of the drive. This can be the case when the drive was previously in use
on a different computer or on a different hard disk controller. You may use
the PARTINFO utility program to print the contents of the partition tables.
Keep in mind that the actual geometry of the drive and the "apparent geometry"
assigned to the drive by the operating system may be different.
Error #110 - Partition table number of sectors is inconsistent
The hard drive partition table contains erroneous values. The partition table
redundantly contains two descriptions of the size of the partition. The two
descriptions should agree, but do not. You may use the PARTINFO utility
program to print the contents of the partition tables.
This error is serious if the drive is used by both DOS and OS/2. Of the two
descriptions of the size, DOS uses one and OS/2 uses the other. Data loss
is likely once the partition is nearly full. This error can occur if DOS and
OS/2 disagree as to the apparent geometry of the drive.
Error #111 - Logical partition starts outside Extended
The hard drive partition table contains erroneous values. All logical
partitions must be wholly contained inside the extended partition. You may
use the PARTINFO utility program to print the contents of the partition
tables.
Backup the offending partitions, delete and create them again, and then
restore the partition contents. This will create new, error-free
partition tables. You may need to use the FDISK from a fairly new
version of DOS. OS/2's FDISK will often see the same corruption that
PartitionMagic sees and silently refuse to make changes. Older versions of
DOS's FDISK may refuse to delete HPFS or hidden partitions.
Error #112 - Logical partition ends outside Extended
See error #111.
Error #113 - Partitions overlap
The hard drive partition table contains erroneous values. Data partitions can
not overlap, otherwise writing to one may destroy data in another. You may
use the PARTINFO utility program to print the contents of the partition
tables.
This error is often the result of an OS/2 FDISK bug. If free space exists
within the extended partition (typically as a result of using DOS's FDISK),
OS/2's FDISK will allow creation of a primary that overlaps the extended
partition. Subsequently using DOS's FDISK allows creation of a logical drive
in the same space occupied by the overlapping primary.
If a primary partition overlaps the end of the extended partition, but not any
logical partitions within the extended, it is possible to patch the partition
table to fix the problem. However, an incorrect patch could destroy all data
in all partitions of the drive. Only qualified individuals should attempt
this repair.
Those without the qualifications to patch the partition table can backup data
from all partitions, delete all the partitions, re-create the partitions, and
restore the data.
Error #116 - Partition table Begin and Start inconsistant
The hard drive partition table contains erroneous values. The partition table
redundantly contains two descriptions of the starting sector of the partition.
The two descriptions should agree, but do not. You may use the PARTINFO
utility program to print the contents of the partition tables.
This error is serious if the drive is used by both DOS and OS/2. Of the two
descriptions of the starting sector, DOS uses one and OS/2 uses the other.
Data loss is likely once the partition is nearly full. This error can occur
if DOS and OS/2 disagree as to the apparent geometry of the drive.
Error #117 - Partition's drive letter can not be identified
Under OS/2 PartitionMagic must know the drive letter for each partition before
changes can safely be made. There may be a driver on your system that changes
the drive letters from the defaults. Or you may have partitions that don't
have serial numbers. For whatever reason, PartitionMagic could not identify
the correct drive letters for your partitions.
Error #118 - Two partitions have the same serial number
In certain instances, PartitionMagic requires that all partitions have unique
serial numbers. This typically happens when a drive letter change has occurred
on your system as a result of loading a driver for disk compression or drive
letter remapping. Stacker is one driver that assigns a non-unique serial
number to stacked volumes.
If you get this error under OS/2 and you have Stacker, use the LABEL command
to give each stacked volume a volume name of the form "STACVOL xxx", where xxx
is unique for each volume. Do not set the volume label of the host partition
(containing the "STACVOL*.*" hidden file) to anything starting with STACVOL.
Once each stacked volume has been so named, PartitionMagic will ignore
non-unique serial numbers on the stacked volumes. After using PartitionMagic,
you can change the volume labels back to whatever name you prefer.
You may use the SNUTIL utility, under DOS, to change the serial numbers of
physical FAT partitions. SNUTIL can not be used for HPFS partitions, network
volumes, compressed volumes, or other volumes that are not physical
partitions.
Error #119 - A drive has been formatted since starting PartitionMagic
PartitionMagic reads information about each partition into memory when
starting. If you switch to another window and format a partition, you must
quit PartitionMagic and start it again so that PartitionMagic can see the
change.
Errors #500 to #505 - (Various Check Disk Errors)
These are mainly Check errors. See the information above about Check errors
and CHKDSK.
Error #505 - Path was invalid
Error #506 - Not enough free space on partition to shrink
A certain amount of free space, dependent on the data already on the drive, is
required to shrink the partition. Try deleting unused or duplicate files in
the partition before attempting the operation again.
Error #508 - As specified, the operation does not change the partition
You have entered a value that is either the same, or when rounded to the
required cylinder boundary, rounds to the same value as the partition
presently is. Enter a larger change.
Error #950 - Unable to detect any disk drives
No partitionable drives were found on your computer. Floppy drives and
certain removable media drives do not support multiple partitions on one disk.
Such drives can not be used by PartitionMagic.
Error #951 - User entered an invalid value
The value entered is either outside the given range, or when rounded to the
required cylinder boundary, is outside the legal range for the operation
specified. Check the displayed range and reenter the value.
Error #952 - Value entered is the same as the current value
See error #508.
Error #953 - Need larger change
See error #508.
Errors #1000 to #2999 - (Various Check Disk Errors)
These are mainly Check errors. See the information above about Check errors
and CHKDSK.
|
|
PartitionMagic v. 1.01 (29/3/1995, PowerQuest Corporation) |
Readme/What's new |
README.TXT for PartitionMagic
PartitionMagic by PowerQuest
Version 1.01 for OS/2
Copyright (c) 1994-1995, PowerQuest Corporation
All Rights Reserved. Patent Pending.
This file explains changes made since the printing of the manual.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
-----------------
I. Legal Notices
II. Changing Your Boot Partition
III. Boot Manager
IV. Warnings
V. Drives >1024 Cylinders
VI. Text Mode PQMAGICT.EXE
VII. Code Pages
I. Legal Notices
----------------
The entire risk of the use or the result of the use of this sofware and
documentation remains with the user. No part of this document may be
reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
mechanical, for any purpose, except as expressed in the Software License
Agreement.
Copyright (c) 1994-1995, PowerQuest Corporation. All rights reserved. This
software and documentation are copyrighted. All other rights, including
ownership of the software, are reserved to PowerQuest Corporation. This
software is protected by one or more pending patents.
PartitionMagic, PowerQuest, the PowerQuest Mark, Partition Map, and Partition
List are trademarks of PowerQuest Corporation.
II. Changing Your Boot Partition
--------------------------------
If you want to modify your OS/2 boot partition, you must boot from an
alternate source. If you have multiple boot partitions, boot from a partition
other than the partition you want to modify. If your hard drive contains less
than 1024 cylinders, you can start and operate PartitionMagic from DOS. See p.
19 in the *User Guide*. You can also use PartitionMagic from OS/2 Maintenance
Mode. See p. 19 in the *User Guide*. When booting Warp, a change is made to
step 3: press F3 instead of ESC to enter Maintenance Mode.
Also, see the material later in this file for information about drives
containing more than 1024 cylinders, and Text Mode (PQMAGICT.EXE).
III. Boot Manager
-----------------
Because of bugs and limitations in OS/2's Boot Manager, moving or resizing a
partition usually causes Boot Manager to malfunction. Boot Manager may delete
partitions from its menu, display partitions with the wrong drive letter, fail
to boot a bootable partition, fail to display a partition, or boot partly from
one partition and partly from another.
We have reported the problems to IBM and hope for their cooperation in finding
permanent solutions to these problems. In the mean time, the work-around is
simple. If you experience any of the above problems with Boot Manager:
1) Boot OS/2. If Boot Manager will not boot, you can boot from your
installation disks.
2) Run FDISK. FDISK does not suffer from the Boot Manager bugs and will
display all your partitions, with the correct drive letters.
3) For any partition that disappeared from the Boot Manager menu, select Add
to Boot Manager Menu. If that option is grayed out, first select Delete from
Boot Manager Menu. This works around Boot Manager's limitation; it can not
track moving partitions.
4) Otherwise, select Change Partition Name on any of the bootable
partitions. This works around the Boot Manager bug that causes Boot Manager to
display wrong drive letters, fail to boot a bootable partition, fail to
display a partition, or boot partly from one partition and partly from
another.
5) Exit FDISK and save the changes.
There is another Boot Manager/FDISK bug that PartitionMagic detects and
handles correctly. Changing the Boot Manager label of a logical partition
using FDISK partially damages the partition tables. The damaged portions are
non-critical for DOS and OS/2. PartitionMagic used to give error 108,
"Partition doesn't end at end of cylinder" and refused to run. PartitionMagic
now diagnoses the damage and extracts the proper information from other
sources in the partition tables. If PartitionMagic makes any changes to the
damaged partition table, PartitionMagic will write repaired tables to the
disk.
IV. Warnings
------------
- Don't forget to backup your hard drive before using PartitionMagic.
- Don't powerdown or prematurely reboot when PartitionMagic is in the middle
of an operation.
- Do not format drives while PartitionMagic is running. PartitionMagic does
not know about the change and does not Move/Resize the partition correctly.
- Do not use the DOS executable of PartitionMagic under Multitasking software
such as Windows or DesqView. It is best to turn off disk caching software when
using the DOS executable.
- It is normal to get an error starting Windows 3.1 stating the swap file is
corrupt. Windows 3.1 is designed knowing that disk utilities may move the
clusters of the swap file. When a move is detected, the error message is
given. To fix the swap file, delete the swap file and create it again. Click
on the 386 Enhanced icon in Control Panel, then on the Virtual Memory button.
- Computers with DMA hardware bugs can corrupt partitions. A Gateway2000 P5-75
is the only computer we've seen this problem on. If you have problems with
applications while other applications access a floppy drive or a network
drive, you have DMA hardware problems and should not use PartitionMagic on
that computer. Beware that if you do have DMA hardware problems, NONE of your
data is safe for long when you run any program--including the operating
system!
- The PartitionMagic DOS executable (PQMAGICD.EXE) uses the same DOS extender
as DOOM. If DOOM will not run on your computer, chances are that PQMAGICD.EXE
will not run either.
V. Drives >1024 Cylinders
-------------------------
If any partitions go past cylinder 1023, you will get error 109, "Partition
ends after end of disk" when running PartitionMagic from DOS or sometimes from
Maintenance Mode. If at all possible, use the Presentation Manager executable
(PQMAGIC.EXE) to modify the drive. Depending on the drivers loaded when
starting Maintenance Mode, OS/2 can access the entire drive. If not, you must
change the CONFIG.SYS used to start Maintenance Mode to include the same hard
disk drivers used by the full OS/2 boot.
VI. Text Mode PQMAGICT.EXE
--------------------------
When you run PartitionMagic in Maintenance Mode, depending on how you started
OS/2, you may get the error, "SYS1804: The system can not find the file
VIOCALLS." To solve this problem, copy VIOCALLS.DLL and PQMAGICT.EXE to a
scratch floppy. Then start PQMAGICT.EXE from the scratch floppy.
You should copy VIOCALLS.DLL from the disk or diskettes you used to boot OS/2.
It can be found in the following locations:
Boot Source VIOCALLS.DLL Location
---------------------- ---------------------
Installation Diskettes Install Disk 1
Utility Diskettes Utility Disk 2
Hard Disk \OS2\DLL
To access physical drives beyond the first four, use the Text Mode executable,
PQMAGICT.EXE.
VII. Code Pages
---------------
This release of PartitionMagic handles 7-bit ASCII filenames. PartitionMagic
does not yet handle full 8-bit character sets such as Code Page 850 or double
byte character sets. Converting a partition can produce incorrectly translated
filenames.
|






Aggiungi un commento